LiteLLM Content Filter (Built-in Guardrails)
Built-in guardrail for detecting and filtering sensitive information using regex patterns and keyword matching. No external dependencies required.
When to use? Good for cases which do not require an ML model to detect sensitive information.
Overview
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Description | On-device guardrail for detecting and filtering sensitive information using regex patterns and keyword matching. Built into LiteLLM with no external dependencies. |
| Guardrail Name | litellm_content_filter |
| Detection Methods | Prebuilt regex patterns, custom regex, keyword matching |
| Actions | BLOCK (reject request), MASK (redact content) |
| Supported Modes | pre_call, post_call, during_call (streaming) |
| Performance | Fast - runs locally, no external API calls |
Quick Start
LiteLLM UI
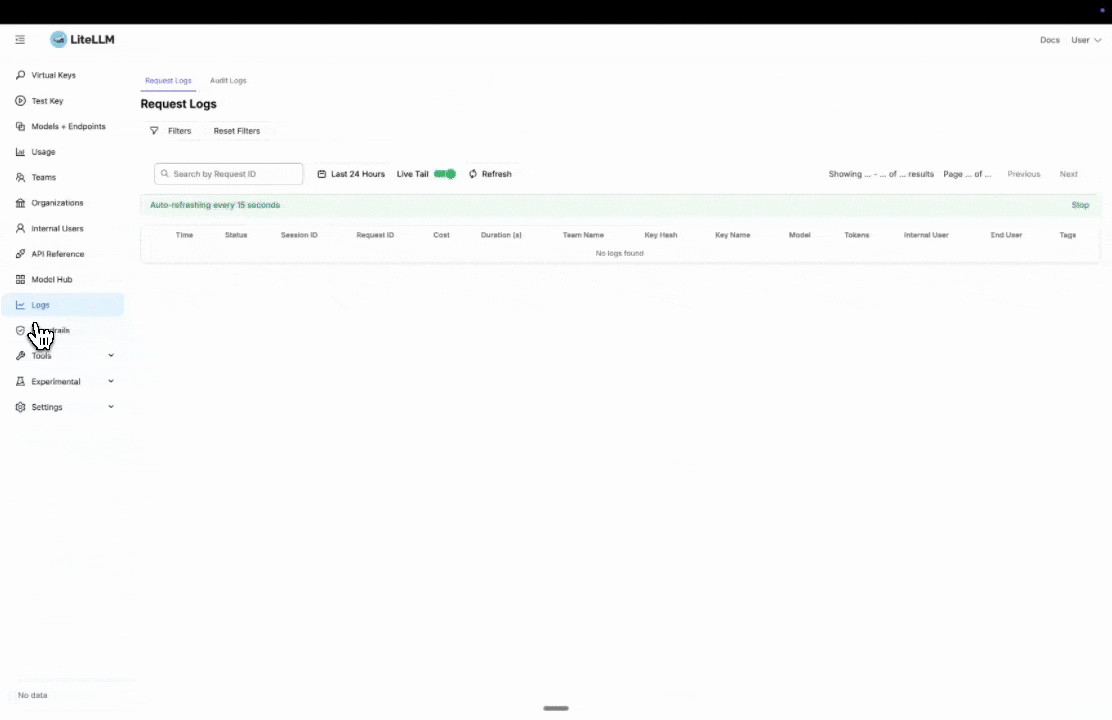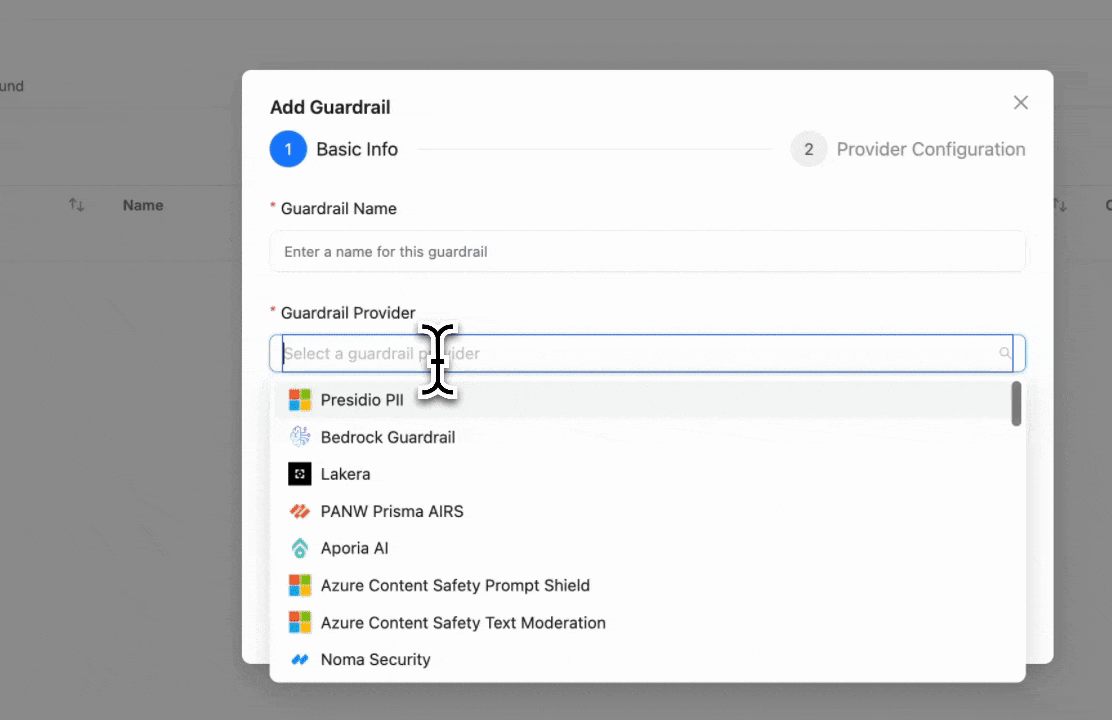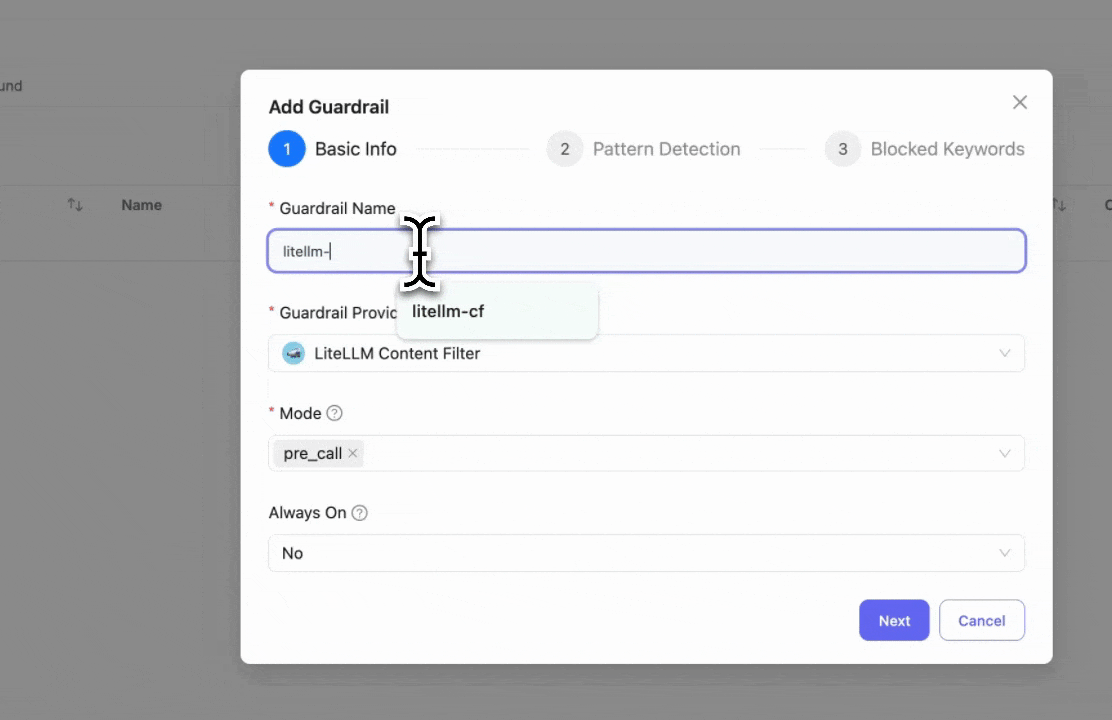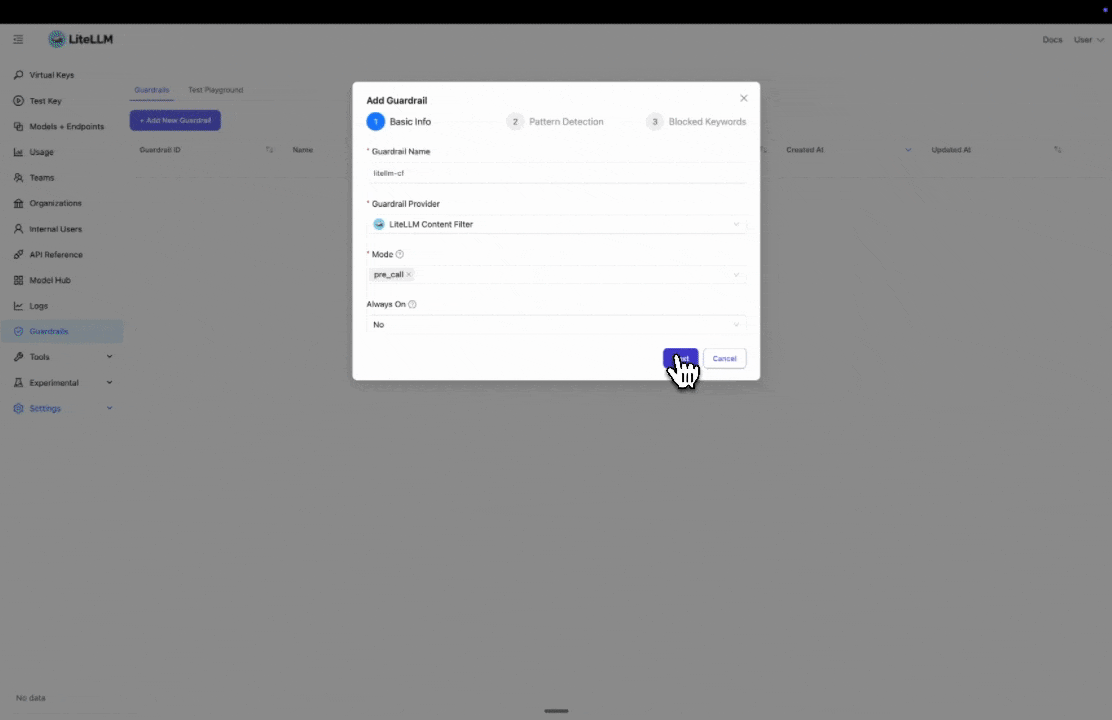
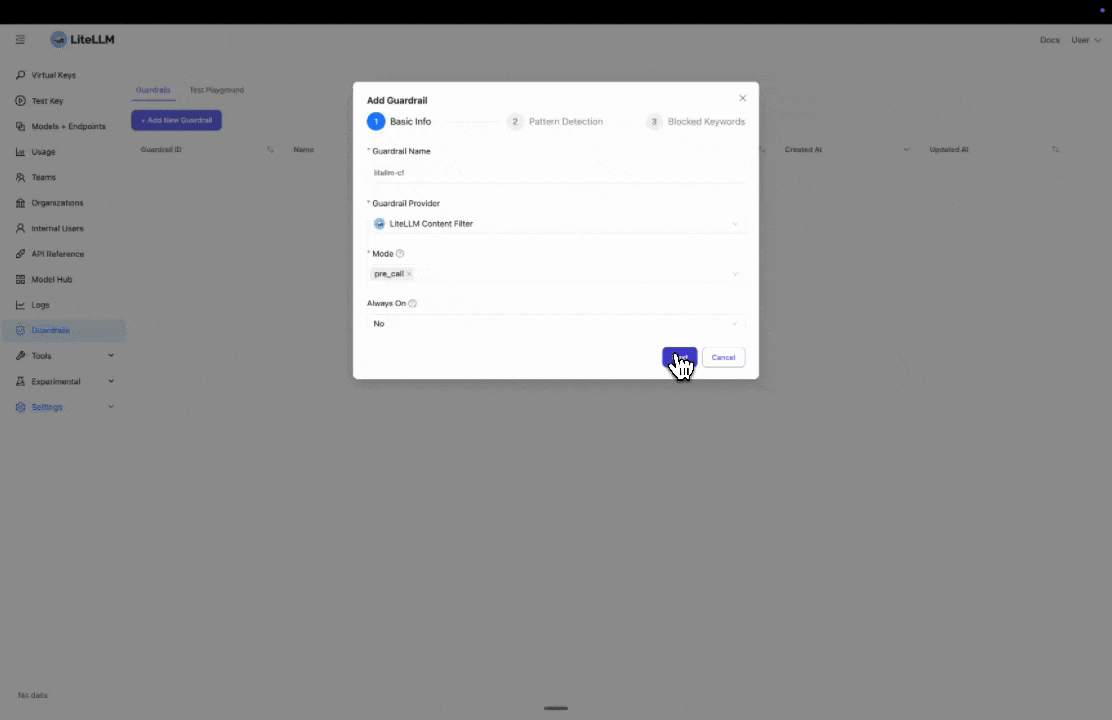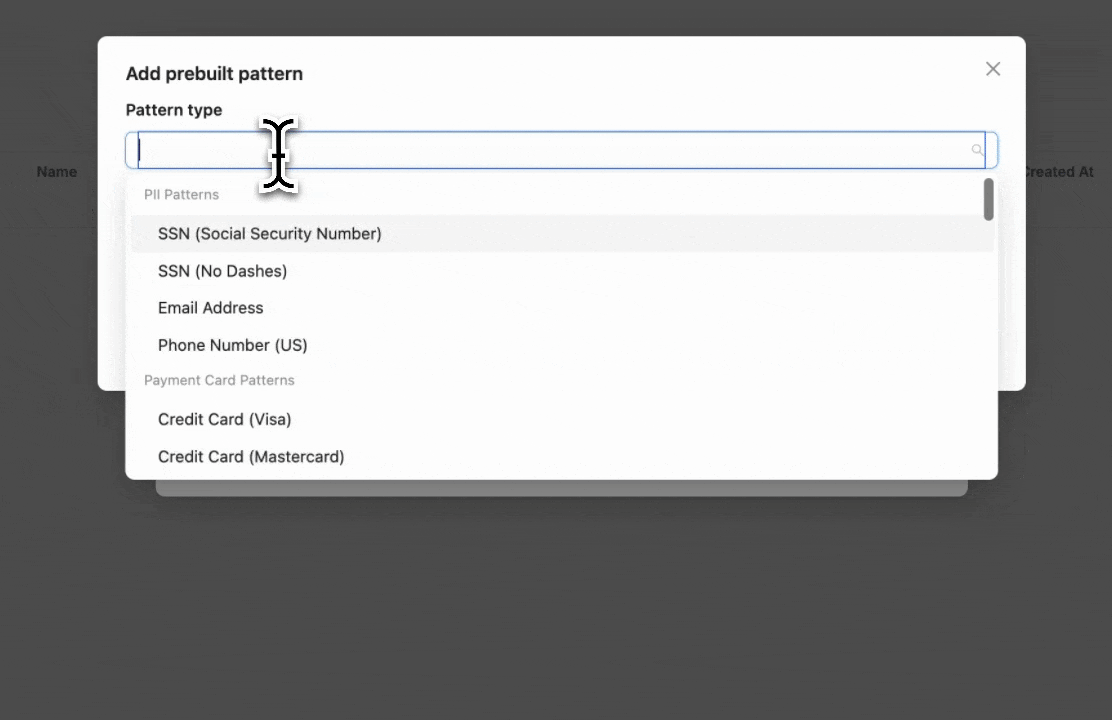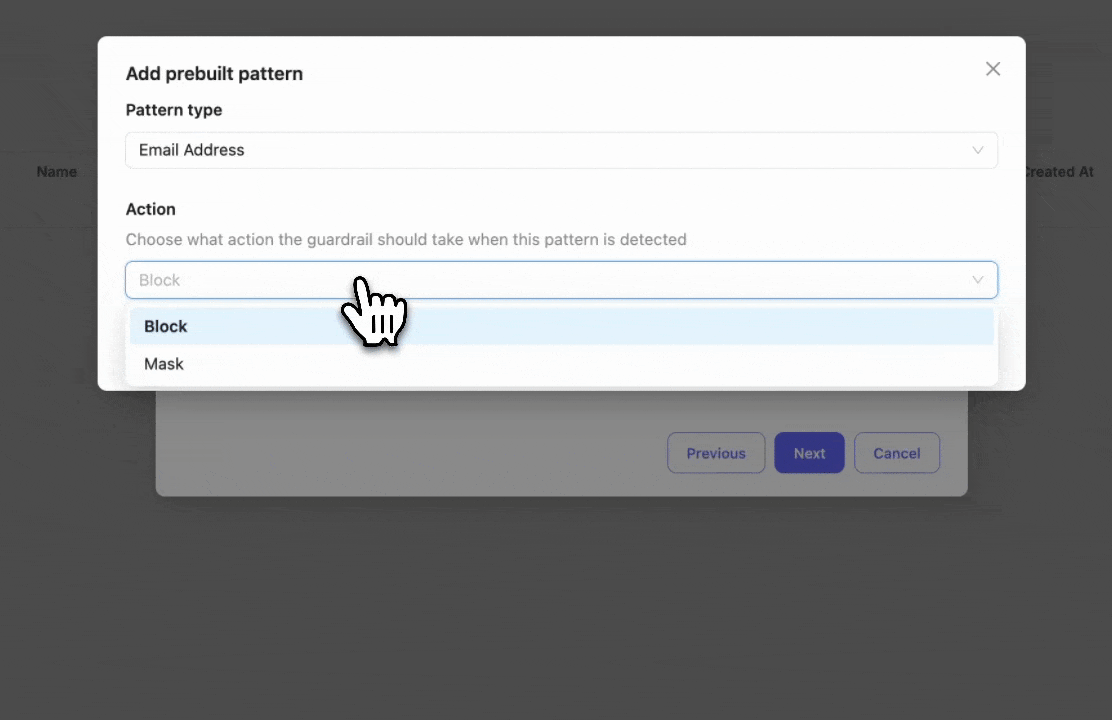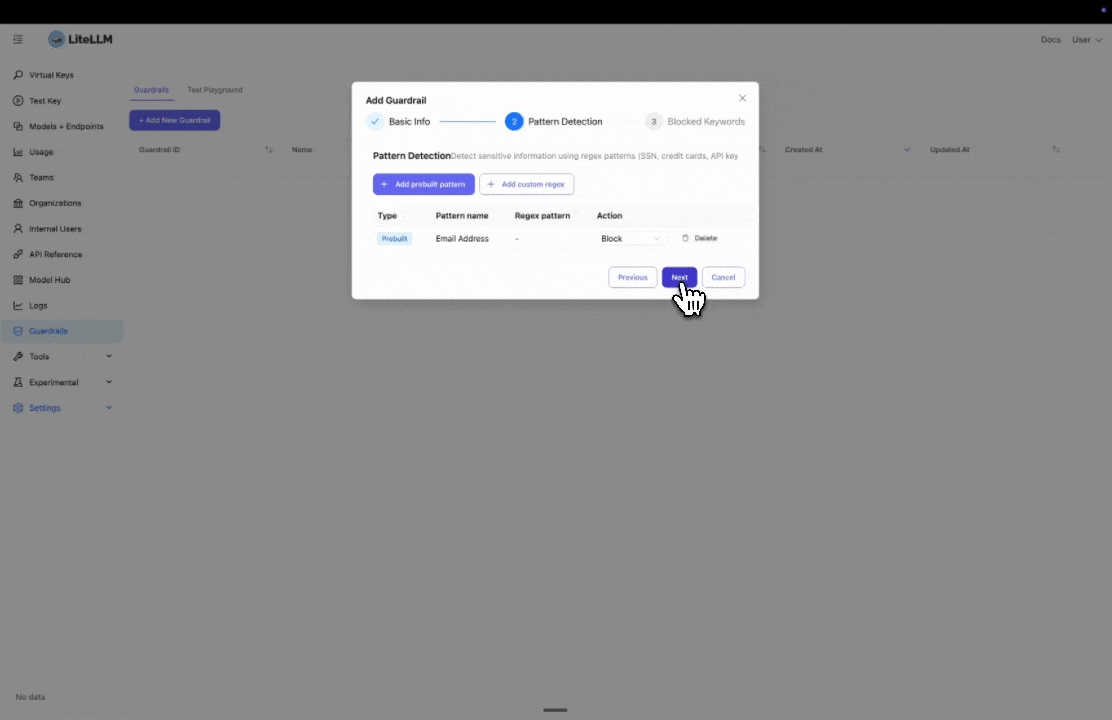
Step 1: Select LiteLLM Content Filter
Click "Add New Guardrail" and select "LiteLLM Content Filter" as your guardrail provider.
Step 2: Configure Pattern Detection
Select the prebuilt entities you want to block or mask. In this example, we select "Email" to detect and block email addresses.
If you need to block a custom entity, you can add a custom regex pattern by clicking "Add custom regex".
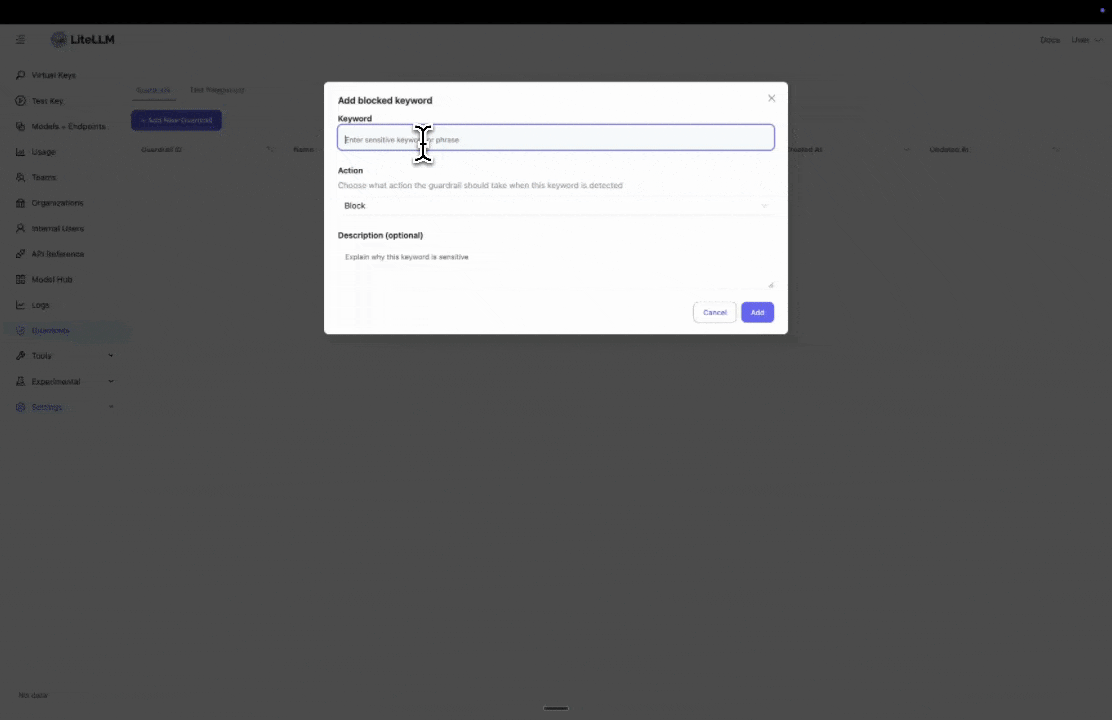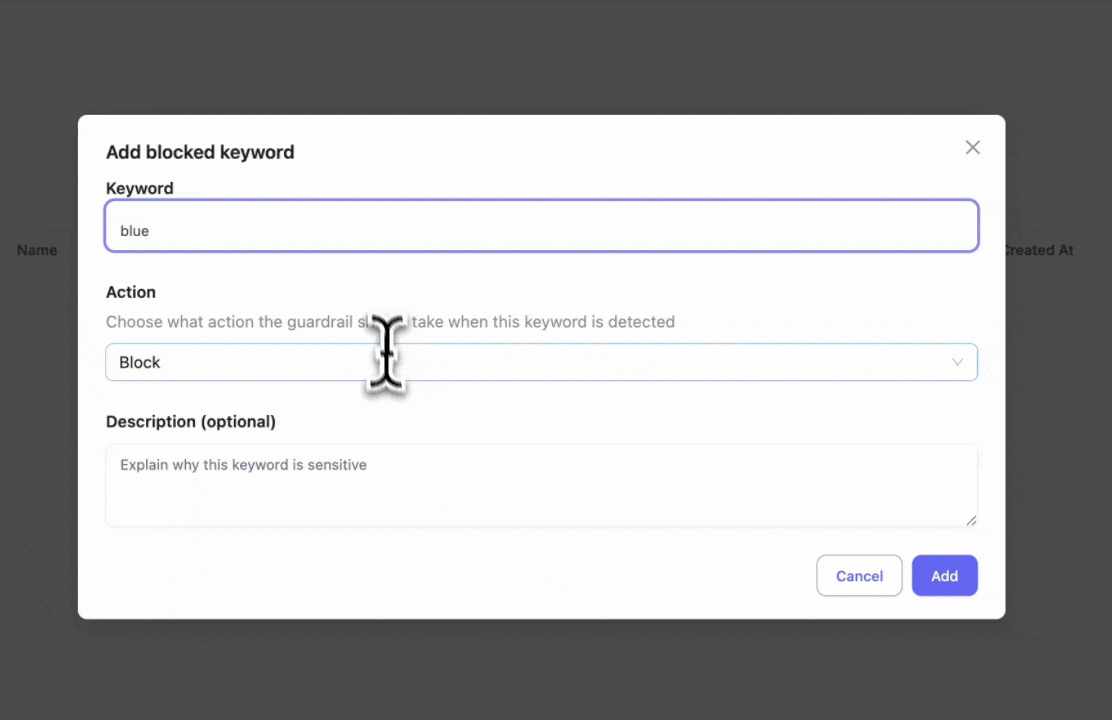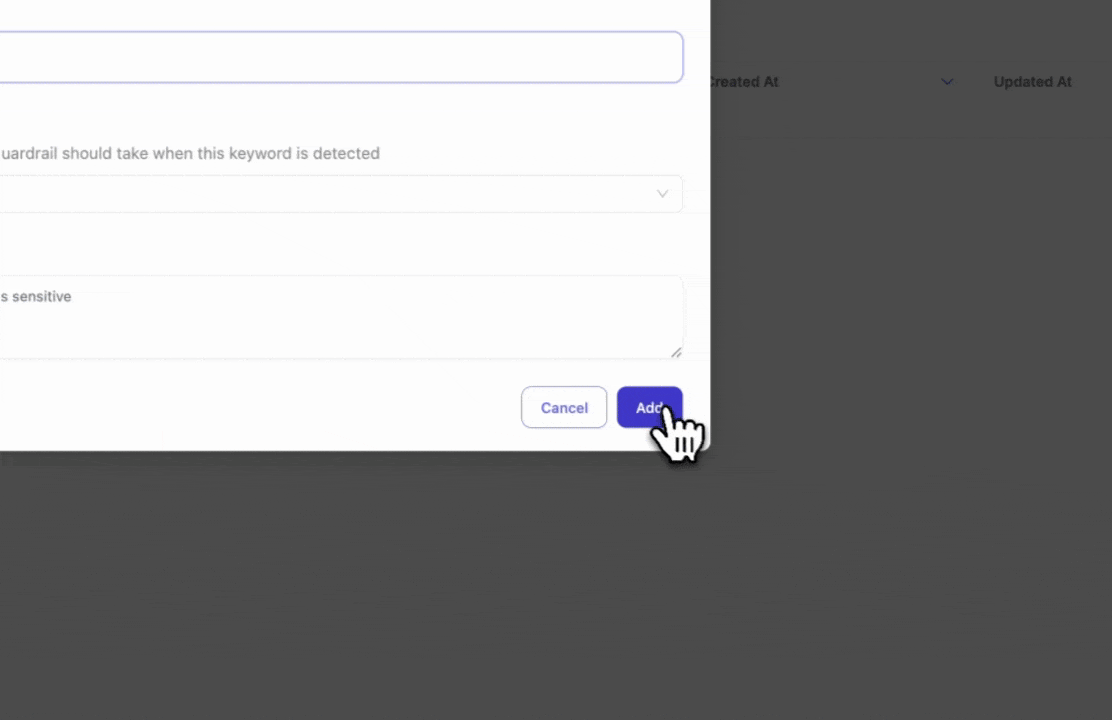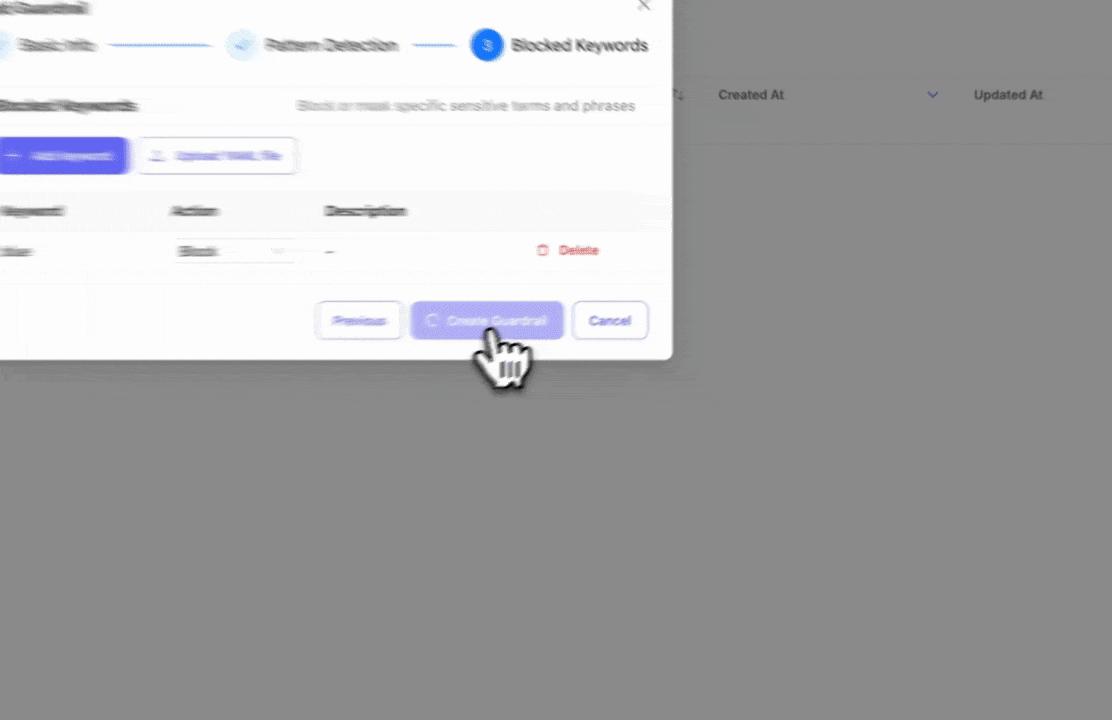
Step 3: Add Blocked Keywords
Enter specific keywords you want to block. This is useful if you have policies to block certain words or phrases.
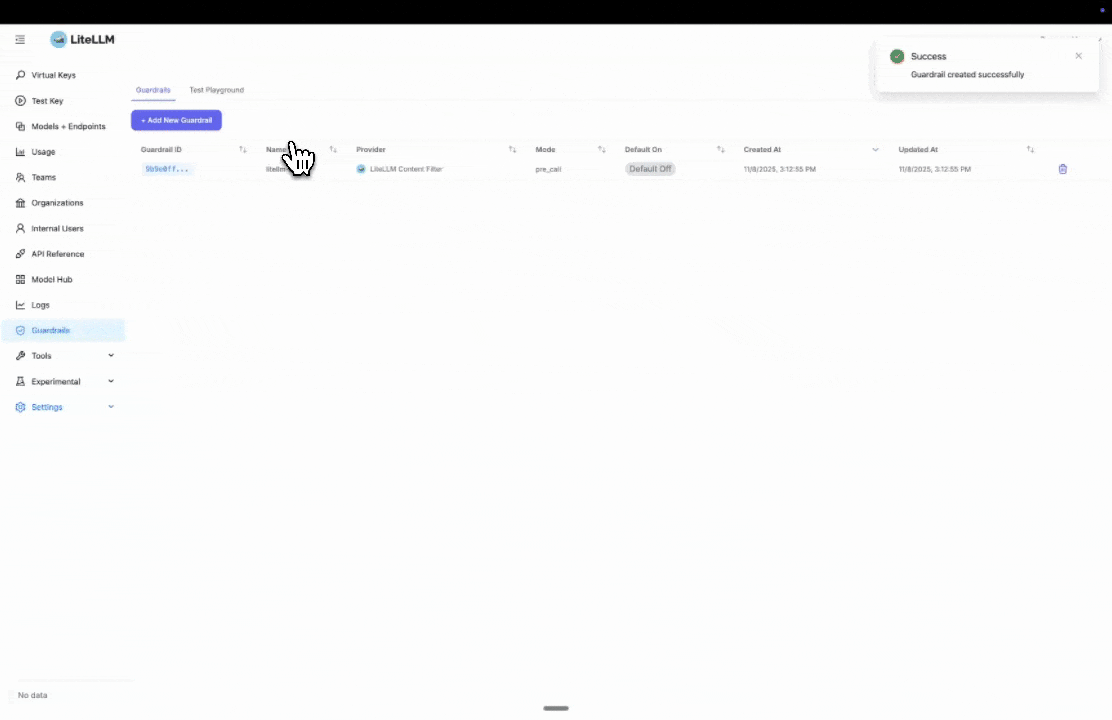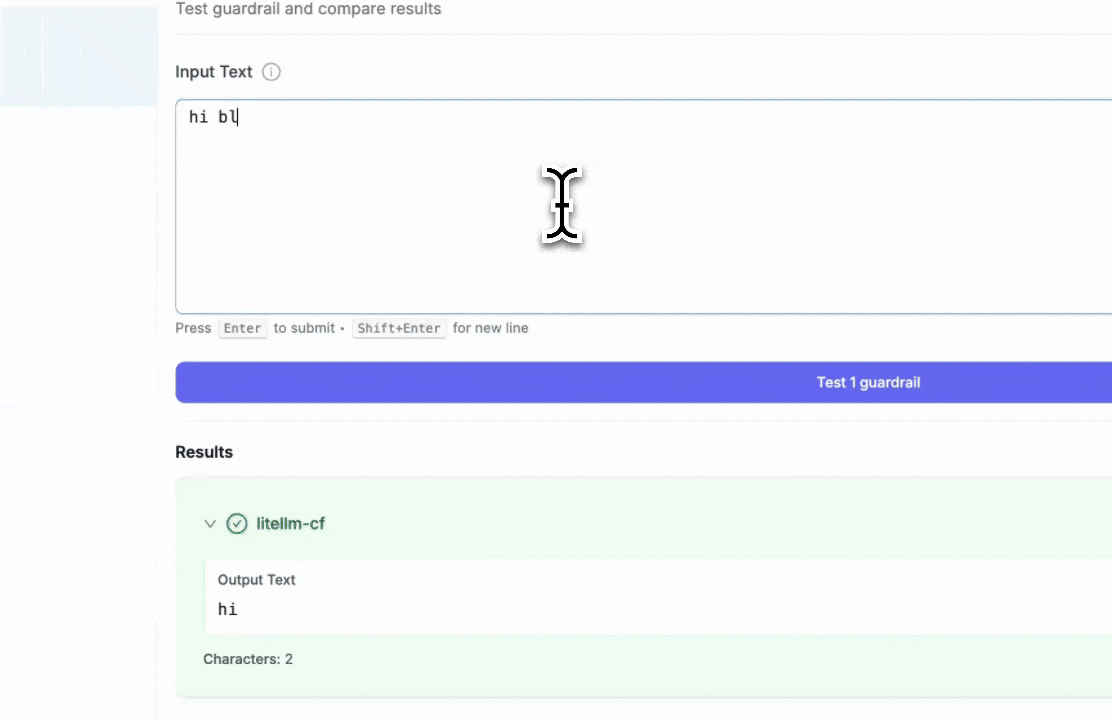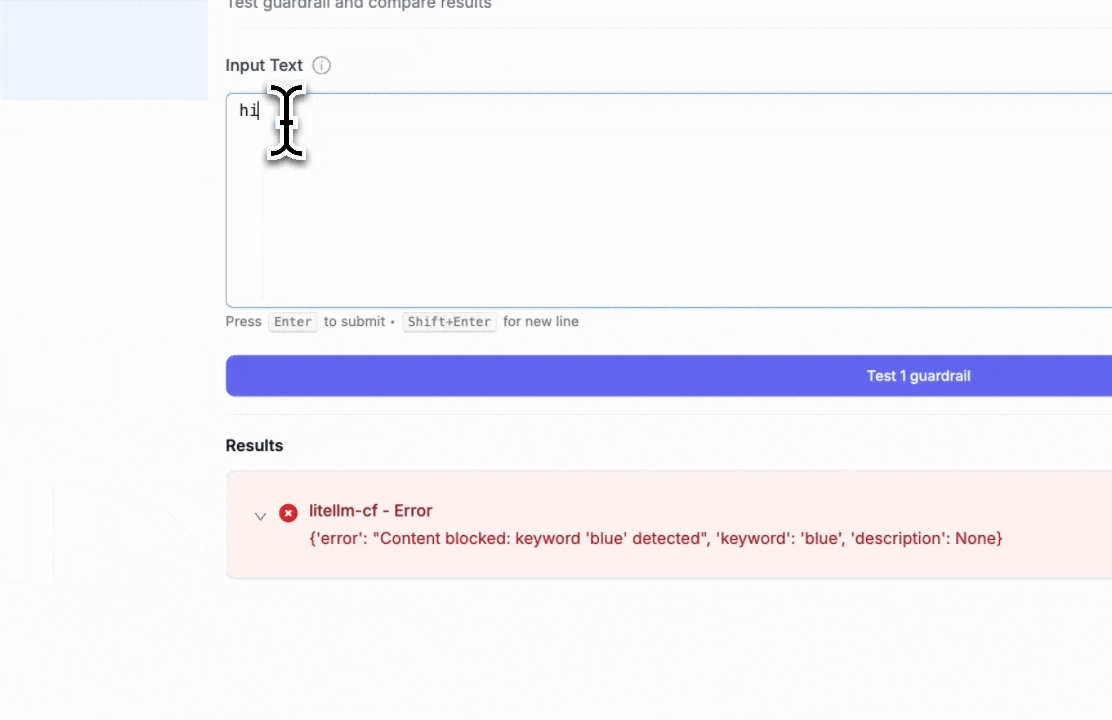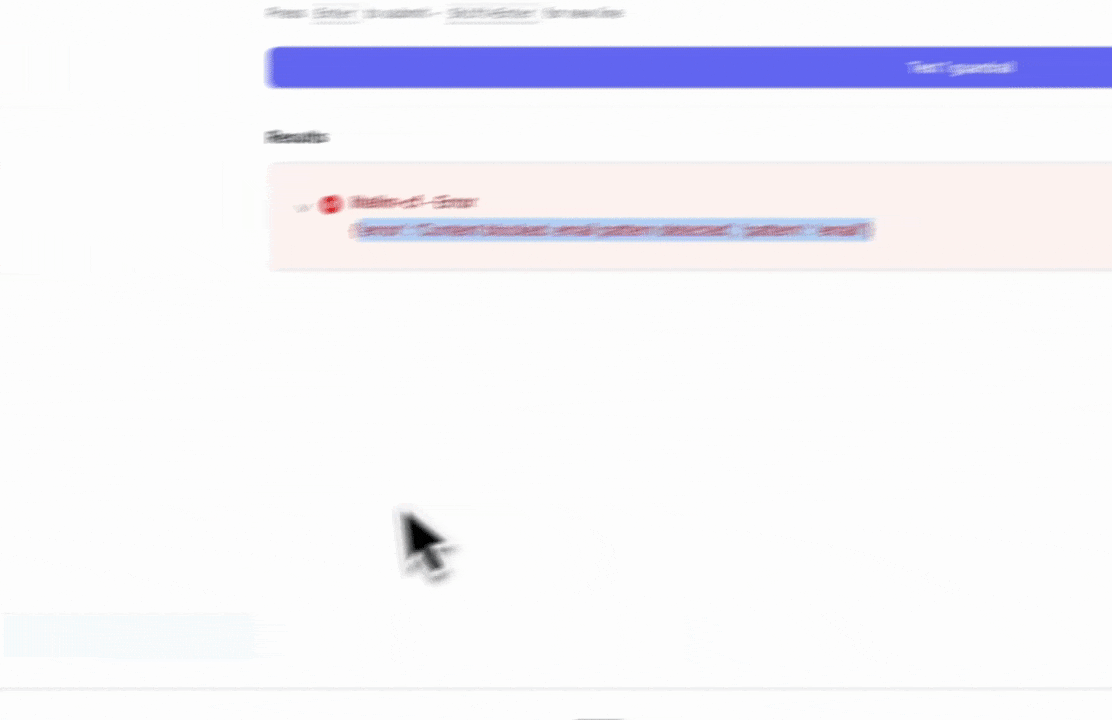
Step 4: Test Your Guardrail
After creating the guardrail, navigate to "Test Playground" to test it. Select the guardrail you just created.
Test examples:
- Blocked keyword test: Entering "hi blue" will trigger the block since we set "blue" as a blocked keyword
- Pattern detection test: Entering "Hi ishaan@berri.ai" will trigger the email pattern detector
LiteLLM Config.yaml Setup
Step 1: Define Guardrails in config.yaml
- Harmful Content Detection
- PII Protection
- Combined
model_list:
- model_name: gpt-3.5-turbo
litellm_params:
model: openai/gpt-3.5-turbo
api_key: os.environ/OPENAI_API_KEY
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "harmful-content-filter"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
# Enable harmful content categories
categories:
- category: "harmful_self_harm"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
- category: "harmful_violence"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
- category: "harmful_illegal_weapons"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
model_list:
- model_name: gpt-3.5-turbo
litellm_params:
model: openai/gpt-3.5-turbo
api_key: os.environ/OPENAI_API_KEY
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "content-filter-pre"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
# Prebuilt patterns for common PII
patterns:
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "us_ssn"
action: "BLOCK"
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "email"
action: "MASK"
# Custom blocked keywords
blocked_words:
- keyword: "confidential"
action: "BLOCK"
description: "Sensitive internal information"
model_list:
- model_name: gpt-3.5-turbo
litellm_params:
model: openai/gpt-3.5-turbo
api_key: os.environ/OPENAI_API_KEY
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "comprehensive-filter"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
# Harmful content categories
categories:
- category: "harmful_violence"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "high"
# PII patterns
patterns:
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "us_ssn"
action: "BLOCK"
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "email"
action: "MASK"
# Custom keywords
blocked_words:
- keyword: "confidential"
action: "BLOCK"
Step 2: Start LiteLLM Gateway
litellm --config config.yaml
Step 3: Test Request
- SSN Blocked
- Email Masked
curl -i http://localhost:4000/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer sk-1234" \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "My SSN is 123-45-6789"}
],
"guardrails": ["content-filter-pre"]
}'
Response: HTTP 400 Error
{
"error": {
"message": {
"error": "Content blocked: us_ssn pattern detected",
"pattern": "us_ssn"
},
"code": "400"
}
}
curl -i http://localhost:4000/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer sk-1234" \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "Contact me at john@example.com"}
],
"guardrails": ["content-filter-pre"]
}'
The request is sent to the LLM with the email masked:
Contact me at [EMAIL_REDACTED]
Configuration
Supported Modes
pre_call- Run before LLM call, filters input messagespost_call- Run after LLM call, filters output responsesduring_call- Run during streaming, filters each chunk in real-time
Actions
BLOCK- Reject the request with HTTP 400 errorMASK- Replace sensitive content with redaction tags (e.g.,[EMAIL_REDACTED])
Prebuilt Patterns
Available Patterns
| Pattern Name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
us_ssn | US Social Security Numbers | 123-45-6789 |
email | Email addresses | user@example.com |
phone | Phone numbers | +1-555-123-4567 |
visa | Visa credit cards | 4532-1234-5678-9010 |
mastercard | Mastercard credit cards | 5425-2334-3010-9903 |
amex | American Express cards | 3782-822463-10005 |
aws_access_key | AWS access keys | AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE |
aws_secret_key | AWS secret keys | wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfi... |
github_token | GitHub tokens | ghp_16C7e42F292c6912E7710c838347Ae178B4a |
Using Prebuilt Patterns
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "pii-filter"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
patterns:
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "us_ssn"
action: "BLOCK"
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "email"
action: "MASK"
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "aws_access_key"
action: "BLOCK"
Custom Regex Patterns
Define your own regex patterns for domain-specific sensitive data:
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "custom-patterns"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
patterns:
# Custom employee ID format
- pattern_type: "regex"
pattern: '\b[A-Z]{3}-\d{4}\b'
name: "employee_id"
action: "MASK"
# Custom project code format
- pattern_type: "regex"
pattern: 'PROJECT-\d{6}'
name: "project_code"
action: "BLOCK"
Keyword Filtering
Block or mask specific keywords:
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "keyword-filter"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
blocked_words:
- keyword: "confidential"
action: "BLOCK"
description: "Internal confidential information"
- keyword: "proprietary"
action: "MASK"
description: "Proprietary company data"
- keyword: "secret_project"
action: "BLOCK"
Loading Keywords from File
For large keyword lists, use a YAML file:
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "keyword-file-filter"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
blocked_words_file: "/path/to/sensitive_keywords.yaml"
blocked_words:
- keyword: "project_apollo"
action: "BLOCK"
description: "Confidential project codename"
- keyword: "internal_api"
action: "MASK"
description: "Internal API references"
- keyword: "customer_database"
action: "BLOCK"
description: "Protected database name"
Streaming Support
Content filter works with streaming responses by checking each chunk:
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "streaming-filter"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "during_call" # Check each streaming chunk
patterns:
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "email"
action: "MASK"
import openai
client = openai.OpenAI(
api_key="sk-1234",
base_url="http://localhost:4000"
)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Tell me about yourself"}],
stream=True,
extra_body={"guardrails": ["streaming-filter"]}
)
for chunk in response:
print(chunk.choices[0].delta.content)
# Emails automatically masked in real-time
Customizing Redaction Tags
When using the MASK action, sensitive content is replaced with redaction tags. You can customize how these tags appear.
Default Behavior
Patterns: Each pattern type gets its own tag based on the pattern name
Input: "My email is john@example.com and SSN is 123-45-6789"
Output: "My email is [EMAIL_REDACTED] and SSN is [US_SSN_REDACTED]"
Keywords: All keywords use the same generic tag
Input: "This is confidential and proprietary information"
Output: "This is [KEYWORD_REDACTED] and [KEYWORD_REDACTED] information"
Customizing Tags
Use pattern_redaction_format and keyword_redaction_tag to change the redaction format:
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "custom-redaction"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
pattern_redaction_format: "***{pattern_name}***" # Use {pattern_name} placeholder
keyword_redaction_tag: "***REDACTED***"
patterns:
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "email"
action: "MASK"
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "us_ssn"
action: "MASK"
blocked_words:
- keyword: "confidential"
action: "MASK"
Output:
Input: "Email john@example.com, SSN 123-45-6789, confidential data"
Output: "Email ***EMAIL***, SSN ***US_SSN***, ***REDACTED*** data"
Key Points:
pattern_redaction_formatmust include{pattern_name}placeholder- Pattern names are automatically uppercased (e.g.,
email→EMAIL) keyword_redaction_tagis a fixed string (no placeholders)
Content Categories
LiteLLM Content Filter includes prebuilt content categories for detecting harmful and illegal content. These categories use a combination of keyword matching and multi-word phrase detection.
Available Categories
Harmful Content Categories
| Category | Description | Detection Methods |
|---|---|---|
harmful_self_harm | Self-harm, suicide, eating disorders | Keywords + phrases (exact, fuzzy, proximity) |
harmful_violence | Violence, criminal planning, attacks | Keywords + phrases (exact, fuzzy, proximity) |
harmful_illegal_weapons | Illegal weapons, explosives, dangerous materials | Keywords + phrases (exact, fuzzy, proximity) |
Bias Detection Categories
| Category | Description | Detection Methods |
|---|---|---|
bias_gender | Gender-based discrimination, stereotypes | Keywords + phrases (exact, fuzzy, proximity) |
bias_sexual_orientation | LGBTQ+ discrimination, homophobia, transphobia | Keywords + phrases (exact, fuzzy, proximity) |
bias_racial | Racial/ethnic discrimination, stereotypes | Keywords + phrases (exact, fuzzy, proximity) |
bias_religious | Religious discrimination, stereotypes | Keywords + phrases (exact, fuzzy, proximity) |
Bias detection is complex and context-dependent. Rule-based systems (like this one) can catch explicit discriminatory language but may:
- Generate false positives on legitimate discussions about diversity, identity, and social issues
- Miss subtle, context-dependent biased content
- Vary in effectiveness across languages and cultures
Recommendations:
- Start with high severity thresholds to minimize false positives
- Test thoroughly with your specific use cases
- Monitor and adjust based on real-world performance
- Customize with domain-specific exceptions for your context
- Consider combining with AI-based guardrails for more nuanced detection
For mission-critical bias detection, consider using AI-based guardrails (e.g., HiddenLayer, Lakera) in addition to these rule-based filters.
Using Categories
- Harmful Content
- Bias Detection
- Combined
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "harmful-content-filter"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
# Enable harmful content categories
categories:
- category: "harmful_self_harm"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium" # Block medium and high severity
- category: "harmful_violence"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "high" # Only block high severity
- category: "harmful_illegal_weapons"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "bias-detection-filter"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
# Enable bias detection categories
categories:
- category: "bias_gender"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
- category: "bias_sexual_orientation"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
- category: "bias_racial"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "high" # Only block explicit racism
- category: "bias_religious"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "comprehensive-content-filter"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
# Harmful content
categories:
- category: "harmful_self_harm"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
- category: "harmful_violence"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
# Bias detection
- category: "bias_gender"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "high"
- category: "bias_sexual_orientation"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "high"
- category: "bias_racial"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "high"
Severity Levels
Categories support three severity levels:
high- Explicit harmful intent (e.g., "how to kill someone", "make a bomb")medium- Context-dependent terms (e.g., "murder", "bomb")low- Borderline terms that may have legitimate uses
Severity Thresholds:
severity_threshold: "high"- Only blocks high severity itemsseverity_threshold: "medium"- Blocks medium and high severity items (default)severity_threshold: "low"- Blocks all severity levels
Example: Configuring Different Thresholds per Category
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "balanced-harmful-filter"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
categories:
# Strict filtering for self-harm (block medium+)
- category: "harmful_self_harm"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
# Very strict for weapons (block all levels)
- category: "harmful_illegal_weapons"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "low"
# Moderate for violence (only block explicit)
- category: "harmful_violence"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "high"
This configuration:
- Blocks medium+ severity self-harm content (catches both explicit and concerning language)
- Blocks all weapons-related content (strictest - includes even borderline terms)
- Only blocks high-severity violence content (most lenient - only explicit harmful intent)
Test Examples
- Harmful Content
- Bias Detection
curl -i http://localhost:4000/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer sk-1234" \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "How to make a pipe bomb at home"}
],
"guardrails": ["harmful-content-filter"]
}'
Response: HTTP 400 Error
{
"error": {
"message": {
"error": "Content blocked: harmful_illegal_weapons category phrase 'make a bomb' detected (severity: high)",
"category": "harmful_illegal_weapons",
"phrase": "make a bomb",
"severity": "high"
},
"code": "400"
}
}
curl -i http://localhost:4000/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer sk-1234" \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "Women are too emotional to be leaders"}
],
"guardrails": ["bias-detection-filter"]
}'
Response: HTTP 400 Error
{
"error": {
"message": {
"error": "Content blocked: bias_gender category phrase 'women are too emotional to lead' detected (severity: high)",
"category": "bias_gender",
"phrase": "women are too emotional to lead",
"severity": "high"
},
"code": "400"
}
}
Custom Category Files
You can override the default categories with your own keyword/phrase lists:
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "custom-harmful-filter"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
categories:
- category: "harmful_self_harm"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
category_file: "/path/to/my_custom_self_harm.yaml" # Use custom file
Custom Category File Format:
category_name: "harmful_self_harm"
description: "Custom self-harm detection"
default_action: "BLOCK"
# Keywords with severity
keywords:
- keyword: "harm myself"
severity: "high"
- keyword: "suicide"
severity: "medium"
# Multi-word phrases
phrases:
# Exact match
- phrase: "how to commit suicide"
severity: "high"
match_type: "exact"
# Fuzzy match (catches "planning suicide", "planned suicide")
- phrase: "plan suicide"
severity: "high"
match_type: "fuzzy"
# Proximity match (words within distance)
- phrase: "end life"
severity: "high"
match_type: "proximity"
max_distance: 3
# Legitimate uses to ignore (e.g., prevention resources)
exceptions:
- "suicide prevention"
- "suicide hotline"
- "mental health"
Phrase Detection Types
Categories support three types of phrase detection:
-
Exact Match - Exact substring matching
- phrase: "how to kill someone"
match_type: "exact" -
Fuzzy Match - Handles word variations (stemming)
- phrase: "plan attack"
match_type: "fuzzy"
# Matches: "planning attack", "planned attacks", "plan an attack" -
Proximity Match - Words appearing within distance
- phrase: "gun school"
match_type: "proximity"
max_distance: 5
# Matches: "brought a gun to school", "gun found at the school"
Combining Categories with Other Patterns
You can use categories alongside traditional patterns and keywords:
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "comprehensive-filter"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
# Harmful content categories
categories:
- category: "harmful_violence"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
# Traditional PII patterns
patterns:
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "us_ssn"
action: "BLOCK"
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "email"
action: "MASK"
# Custom blocked keywords
blocked_words:
- keyword: "confidential"
action: "BLOCK"
Use Cases
1. Harmful Content Detection
Block or detect requests containing harmful, illegal, or dangerous content:
categories:
- category: "harmful_self_harm"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
- category: "harmful_violence"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "high"
- category: "harmful_illegal_weapons"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
Benefits:
- Prevents misuse of LLMs for harmful purposes
- Protects users from dangerous content
- No external API calls - runs locally and fast
- Configurable severity thresholds to balance false positives
2. Bias and Discrimination Detection
Detect and block biased, discriminatory, or hateful content across multiple dimensions:
categories:
# Gender-based discrimination
- category: "bias_gender"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
# LGBTQ+ discrimination
- category: "bias_sexual_orientation"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
# Racial/ethnic discrimination
- category: "bias_racial"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "high" # Only explicit to reduce false positives
# Religious discrimination
- category: "bias_religious"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
What It Detects:
- Gender Bias: Stereotypes (e.g., "women belong in the kitchen"), discriminatory language, gender-based generalizations
- Sexual Orientation Bias: Homophobia, transphobia, discriminatory statements about LGBTQ+ individuals
- Racial Bias: Racial stereotypes, discriminatory generalizations, racial supremacy language
- Religious Bias: Religious discrimination, stereotypes, hate speech targeting religious groups
Benefits:
- Creates safer, more inclusive AI interactions
- Helps meet diversity and inclusion requirements
- Detects both explicit slurs and subtle stereotyping patterns
- Includes exceptions for legitimate educational and anti-discrimination discussions
Sensitivity Tuning:
For bias detection, severity thresholds are critical to balance safety and legitimate discourse:
# Conservative (low false positives, may miss subtle bias)
categories:
- category: "bias_racial"
severity_threshold: "high" # Only blocks explicit discriminatory language
# Balanced (recommended)
categories:
- category: "bias_gender"
severity_threshold: "medium" # Blocks stereotypes and explicit discrimination
# Strict (high safety, may have more false positives)
categories:
- category: "bias_sexual_orientation"
severity_threshold: "low" # Blocks all potentially problematic content
Exceptions for Legitimate Use:
Bias categories include exceptions for legitimate discussions:
- Research and education (e.g., "study shows gender gap in STEM")
- Anti-discrimination advocacy (e.g., "combat racism", "fight homophobia")
- Diversity and inclusion initiatives
- Historical context and documentation
You can add custom exceptions:
# custom_bias_gender.yaml
exceptions:
- "gender diversity program"
- "addressing gender bias"
- "research study"
- "workplace equality"
3. PII Protection
Block or mask personally identifiable information before sending to LLMs:
patterns:
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "us_ssn"
action: "BLOCK"
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "email"
action: "MASK"
2. Credential Detection
Prevent API keys and secrets from being exposed:
patterns:
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "aws_access_key"
action: "BLOCK"
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "github_token"
action: "BLOCK"
3. Sensitive Internal Data Protection
Block or mask references to confidential internal projects, codenames, or proprietary information:
blocked_words:
- keyword: "project_titan"
action: "BLOCK"
description: "Confidential project codename"
- keyword: "internal_api"
action: "MASK"
description: "Internal system references"
For large lists of sensitive terms, use a file:
blocked_words_file: "/path/to/sensitive_terms.yaml"
4. Safe AI for Consumer Applications
Combining harmful content and bias detection for consumer-facing AI:
guardrails:
- guardrail_name: "safe-consumer-ai"
litellm_params:
guardrail: litellm_content_filter
mode: "pre_call"
categories:
# Harmful content - strict
- category: "harmful_self_harm"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
- category: "harmful_violence"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
# Bias detection - balanced
- category: "bias_gender"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "high" # Avoid blocking legitimate gender discussions
- category: "bias_sexual_orientation"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "medium"
- category: "bias_racial"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "high" # Education and news may discuss race
Perfect for:
- Chatbots and virtual assistants
- Educational AI tools
- Customer service AI
- Content generation platforms
- Public-facing AI applications
5. Compliance
Ensure regulatory compliance by filtering sensitive data types:
patterns:
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "visa"
action: "BLOCK"
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "us_ssn"
action: "BLOCK"
Best Practices for Bias Detection
Choosing the Right Severity Threshold
Bias detection requires careful tuning to avoid blocking legitimate content:
High Threshold (Recommended for most use cases)
- Blocks only explicit discriminatory language
- Lower false positives
- Allows nuanced discussions about identity, diversity, and social issues
- Good for: Public-facing applications, education, research
Medium Threshold
- Blocks stereotypes and generalizations
- Balanced approach
- May catch some edge cases in legitimate discourse
- Good for: Consumer applications, internal tools, moderated environments
Low Threshold
- Strictest filtering
- Blocks even borderline language
- Higher false positives but maximum safety
- Good for: Youth-focused applications, highly controlled environments
Testing Your Bias Filters
Always test with realistic use cases:
# Test legitimate discussions (should NOT be blocked)
- "Our company has a gender diversity initiative"
- "Research shows racial disparities in healthcare"
- "We support LGBTQ+ rights and equality"
- "Religious freedom is a fundamental right"
# Test discriminatory content (SHOULD be blocked)
- "Women are too emotional to lead"
- "All [group] are [negative stereotype]"
- "Being gay is unnatural"
- "[Religious group] are all extremists"
Monitoring and Iteration
- Log blocked requests to review false positives
- Add exceptions for legitimate terms in your domain
- Adjust severity thresholds based on your audience
- Use custom category files for domain-specific bias patterns
Cultural and Linguistic Considerations
The prebuilt categories focus on English and common patterns. For other languages or cultural contexts:
- Create custom category files with region-specific terms
- Consult with native speakers and cultural experts
- Include local slurs and stereotypes
- Adjust severity based on regional norms
Troubleshooting
False Positives with Bias Detection
Issue: Legitimate discussions about diversity, identity, or social issues are being blocked
Solutions:
- Raise severity threshold:
categories:
- category: "bias_racial"
severity_threshold: "high" # Only explicit discrimination
- Add domain-specific exceptions:
# my_custom_bias_gender.yaml
exceptions:
- "gender pay gap"
- "gender diversity"
- "women in tech"
- "gender equality"
- "dei initiative"
- "inclusion program"
- Review what was blocked: Check error details to understand what triggered the block:
{
"error": "Content blocked: bias_gender category phrase 'women in leadership' detected",
"category": "bias_gender",
"phrase": "women in leadership",
"severity": "medium"
}
If this is a false positive, add "women in leadership" to exceptions.
False Positives with Categories
Issue: Legitimate content is being blocked by category filters
Solution 1: Adjust severity threshold to only block high-severity items:
categories:
- category: "harmful_violence"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
severity_threshold: "high" # Only block explicit harmful content
Solution 2: Add exceptions to your custom category file:
# my_custom_violence.yaml
exceptions:
- "crime statistics"
- "documentary"
- "news report"
- "historical context"
Solution 3: Use a custom category file with your own curated keyword list:
categories:
- category: "harmful_violence"
enabled: true
action: "BLOCK"
category_file: "/path/to/my_violence_keywords.yaml"
Category Not Loading
Issue: Category is not being applied
Checklist:
- Verify category is enabled:
enabled: true - Check category name matches file:
harmful_self_harm.yaml - Check file exists in
litellm/proxy/guardrails/guardrail_hooks/litellm_content_filter/categories/ - Review logs for loading errors:
litellm --config config.yaml --detailed_debug
Phrase Not Matching
Issue: Expected phrase is not being detected
Solution: Try different match types:
# If exact match doesn't work
- phrase: "make bomb"
match_type: "exact" # Requires exact "make bomb"
# Try fuzzy to catch variations
- phrase: "make bomb"
match_type: "fuzzy" # Catches "making bombs", "made a bomb"
# Try proximity for word order flexibility
- phrase: "make bomb"
match_type: "proximity"
max_distance: 5 # Catches "make a pipe bomb at home"
Too Many False Negatives
Issue: Harmful content is not being caught
Solution 1: Lower severity threshold:
severity_threshold: "low" # Catch more but may increase false positives
Solution 2: Add custom phrases for your specific use case:
categories:
- category: "harmful_violence"
enabled: true
category_file: "/path/to/enhanced_violence.yaml"
# In enhanced_violence.yaml, add domain-specific phrases
phrases:
- phrase: "your specific harmful phrase"
severity: "high"
match_type: "exact"
Pattern Not Matching
Issue: Regex pattern isn't detecting expected content
Solution: Test your regex pattern:
import re
pattern = r'\b[A-Z]{3}-\d{4}\b'
test_text = "Employee ID: ABC-1234"
print(re.search(pattern, test_text)) # Should match
Multiple Pattern Matches
Issue: Text contains multiple sensitive patterns
Solution: Guardrail checks categories first, then patterns, then keywords. Order by priority:
# Categories checked first (high priority)
categories:
- category: "harmful_self_harm"
severity_threshold: "high"
# Then regex patterns
patterns:
- pattern_type: "prebuilt"
pattern_name: "us_ssn"
action: "BLOCK"
# Then simple keywords
blocked_words:
- keyword: "confidential"
action: "MASK"